AWS Elastic Beanstalk
What Is AWS Elastic Beanstalk?
Amazon Web Services (AWS) comprises dozens of services, each of which exposes an area of functionality. While the variety of services offers flexibility for how you want to manage your AWS infrastructure, it can be challenging to figure out which services to use and how to provision them.
With Elastic Beanstalk, you can quickly deploy and manage applications in the AWS Cloud without worrying about the infrastructure that runs those applications. AWS Elastic Beanstalk reduces management complexity without restricting choice or control. You simply upload your application, and Elastic Beanstalk automatically handles the details of capacity provisioning, load balancing, scaling, and application health monitoring. Elastic Beanstalk uses highly reliable and scalable services that are available in the AWS Free Usage Tier.
Elastic Beanstalk supports applications developed in Java, PHP, .NET, Node.js, Python, and Ruby, as well as different container types for each language. A container defines the infrastructure and software stack to be used for a given environment. When you deploy your application, Elastic Beanstalk provisions one or more AWS resources, such as Amazon EC2 instances. The software stack that runs on your Amazon EC2 instances depends on the container type. For example, Elastic Beanstalk supports two container types for Node.js: a 32-bit Amazon Linux image and a 64-bit Amazon Linux image. Each runs a software stack tailored to hosting a Node.js application. You can interact with Elastic Beanstalk by using the AWS Management Console, the AWS Command Line Interface (AWS CLI), or
eb, a high-level CLI designed specifically for Elastic Beanstalk.
You can also perform most deployment tasks, such as changing the size of your fleet of Amazon EC2 instances or monitoring your application, directly from the Elastic Beanstalk web interface (console).
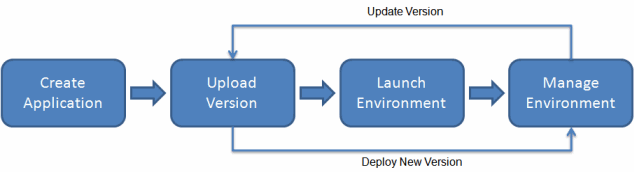
To use Elastic Beanstalk, you create an application, upload an application version in the form of an application source bundle (for example, a Java .war file) to Elastic Beanstalk, and then provide some information about the application. Elastic Beanstalk automatically launches an environment and creates and configures the AWS resources needed to run your code. After your environment is launched, you can then manage your environment and deploy new application versions. The following diagram illustrates the workflow of Elastic Beanstalk.
After you create and deploy your application, information about the application—including metrics, events, and environment status—is available through the AWS Management Console, APIs, or Command Line Interfaces, including the unified AWS CLI. For step-by-step instructions on how to create, deploy, and manage your application using the AWS Management Console.
Elastic Beanstalk provides developers and systems administrators an easy, fast way to deploy and manage their applications without having to worry about AWS infrastructure. If you already know the AWS resources you want to use and how they work, you might prefer AWS CloudFormation to create your AWS resources by creating a template. You can then use this template to launch new AWS resources in the exact same way without having to recustomize your AWS resources. Once your resources are deployed, you can modify and update the AWS resources in a controlled and predictable way, providing the same sort of version control over your AWS infrastructure that you exercise over your software.
Storage
Elastic Beanstalk does not restrict your choice of persistent storage and database service options.
Pricing
There is no additional charge for Elastic Beanstalk. You pay only for the underlying AWS resources that your application consumes.
Comments
Post a Comment